Boston Engineering’s expertise in bio-inspired and magnetic actuation has led to groundbreaking projects across diverse applications. Here are some examples:
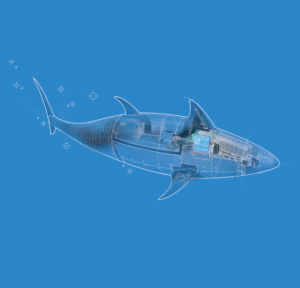
- Bio-Inspired Underwater Vehicles

Purpose: To achieve efficient and stealthy propulsion for underwater exploration.
Actuation Details: Tailored propulsion mechanisms replicate the motion of fish, utilizing flexible fins and oscillatory movements to reduce noise and energy consumption.
Outcome: These vehicles excel in environmental monitoring and infrastructure inspection, offering superior agility and operational efficiency.
- Magnetic Crawlers for Industrial Inspection
Purpose: To inspect and maintain ferrous structures like storage tanks and ship hulls.
Actuation Details: High-strength magnets and precision mobility systems enable robots to adhere to vertical and inverted surfaces while navigating complex geometries.
Outcome: The crawlers enhance safety and efficiency by reducing the need for human intervention in hazardous environments.
- Bio-Inspired Drones
Purpose: To improve aerial maneuverability and endurance.
Actuation Details: Wing designs inspired by birds allow drones to glide and flap efficiently, reducing energy consumption during extended flights.
Outcome: These drones perform exceptionally in applications like wildlife tracking and agricultural monitoring.
- Magnetically Actuated Robots for Hazardous Environments

Purpose: To perform inspections in confined and dangerous spaces.
Actuation Details: Compact robots equipped with magnetic treads navigate pipelines and industrial machinery, detecting faults and performing maintenance.
Outcome: The robots ensure operational reliability while minimizing downtime and risk to personnel.
- Bio-Inspired Robotics for Marine Research
Purpose: To study marine life without disrupting ecosystems.
Actuation Details: Robots use soft, flexible fins to mimic the swimming patterns of marine organisms, enabling them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings.
Outcome: These systems provide researchers with valuable data while minimizing environmental impact.














 Our Robotics Experts, along with software and hardware subject matter experts will enhance your current team or drive your entire project. Don’t leave complex projects or high visibility product launches to chance. Know you’re going to get the results you want by working with industry leaders in design, development, and deployment of innovative products driven by novel engineering. Simply complete the form below and let’s start the Robotics Development Project Conversation
Our Robotics Experts, along with software and hardware subject matter experts will enhance your current team or drive your entire project. Don’t leave complex projects or high visibility product launches to chance. Know you’re going to get the results you want by working with industry leaders in design, development, and deployment of innovative products driven by novel engineering. Simply complete the form below and let’s start the Robotics Development Project Conversation
